CLIMATE ACTION
CLIMATE CHANGE GOVERNANCE
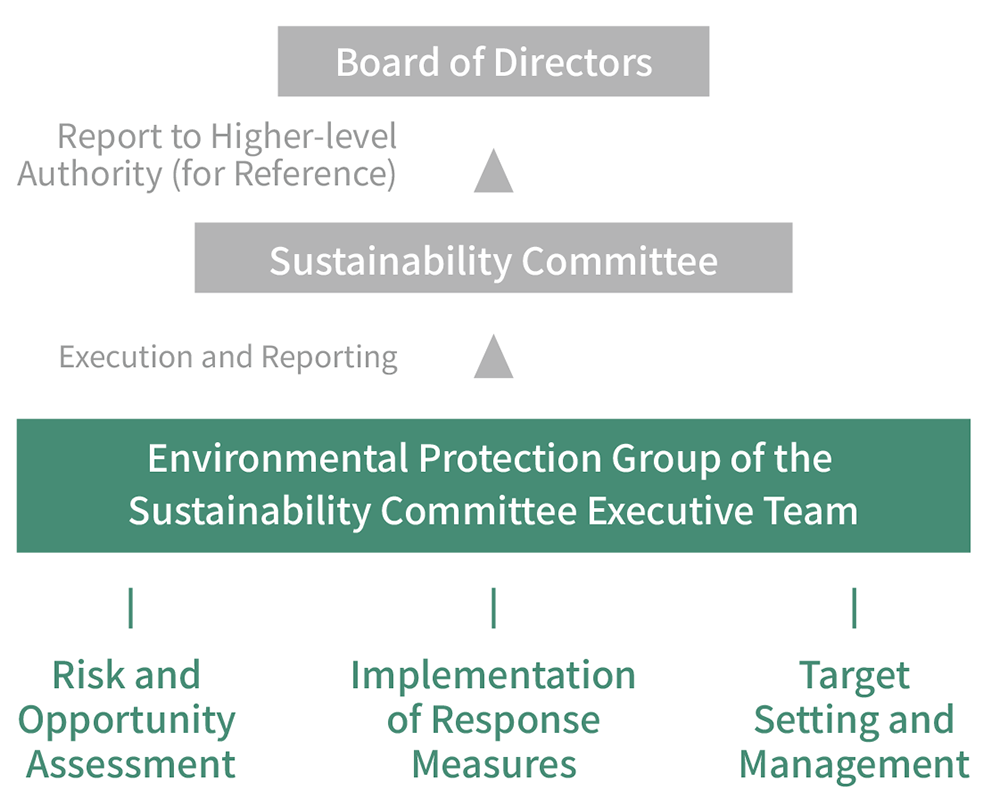
To actively strengthen the sustainability management philosophy and environmental sustainability governance, EGAT has designated the Board of Directors as the highest governance body and, in 2023, approved the establishment of the Sustainability Committee under the Board. The Committee is responsible for overseeing the management and review of sustainability and climate-related issues, integrating climate governance strategies, management systems, and business processes into the Company’s existing governance framework.
Within the Sustainability Committee, the Environmental Protection Group of the Sustainability Committee Executive Team is tasked with managing climate change-related issues. This includes regular monitoring of domestic and international climate policies and environmental regulations, identifying climate-related risks and opportunities, and assessing the potential impacts of climate change on operations. Based on these assessments, EGAT formulates and implements carbon-reduction strategies, energy management, and adaptation measures to ensure the stability and resilience of its operations. In addition, the Sustainability Committee reports the implementation status and results to the Board of Directors on an annual basis and discloses the information externally to enhance corporate transparency and strengthen stakeholder trust, further mitigating the operational impacts of climate-related issues and enhancing the Company’s resilience.
CLIMATE RISK AND OPPORTUNITY ASSESSMENT PROCESS
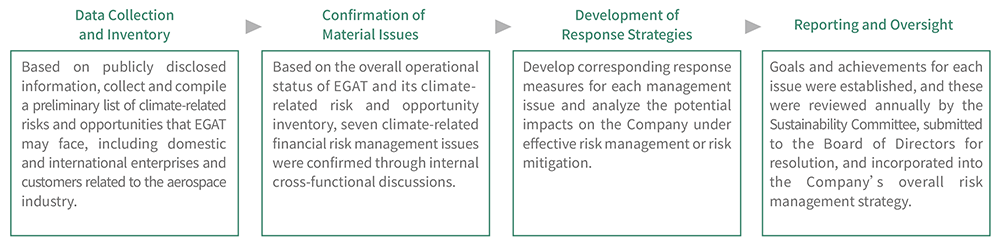
To identify the impacts of climate change on operations and strategic management, EGAT, through its Executive Team under the Sustainability Committee, established a climate risk management process in 2023. The process identified 4 climate-related risks and 3 climate-related opportunities with financial impacts on the Company, and assessed the time horizon Note 1 and value chain impact scope Note 2 of these risks and opportunities. Based on these assessments, corresponding management measures and targets were formulated. The execution of management measures and achievement of targets are regularly reviewed by the Sustainability Committee and submitted to the Board of Directors for resolution, ensuring alignment between climate risk management and the Company’s sustainable development strategy.
Note 1: The impact time horizon is categorized as short-term (1–5 years), medium-term (6–10 years), and long-term (over 10 years).
Note 2: The value chain includes upstream (suppliers), EGAT’s own operations, downstream (customers), and investments.
CLIMATE RISK AND OPPORTUNITY IDENTIFICATION RESULTS
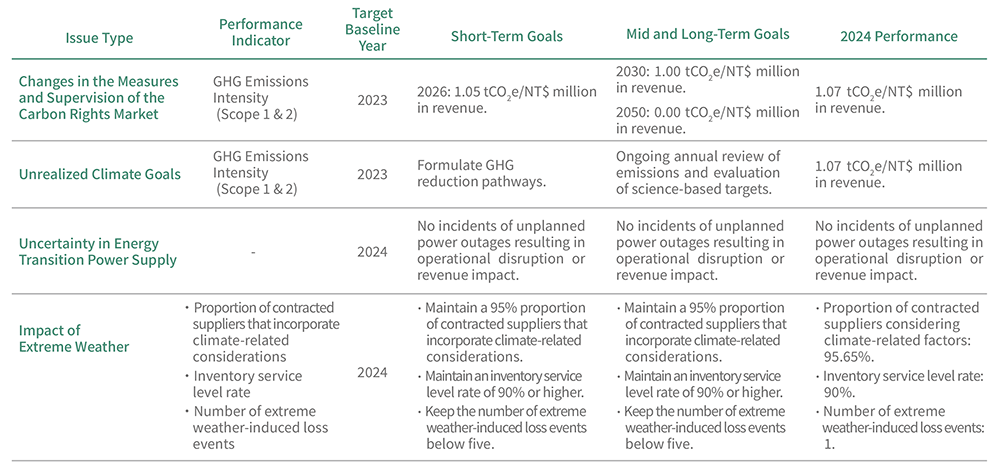
R1 POLICY AND REGULATORY RISK - CHANGES IN THE MEASURES AND SUPERVISION OF THE CARBON RIGHTS MARKET
Description of Risk
Due to government requirements for overall emission control, companies need to purchase carbon credits through carbon market transactions to offset emissions, or pay fines for exceeding emission limits. As the scope of regulatory oversight and carbon pricing per metric ton of emissions is expected to increase annually, EGAT faces the risk of additional corporate cost pressures.
Financial Impact
- Future obligations to pay carbon fees could increase operating costs.
- Increased costs from installing green energy equipment and replacing high-energy-consuming equipment. equipment.
- The expansion and ongoing updates of verification items will lead to increased cost expenditures.
| Affected Parties | Location | Timing of Impact |
|---|---|---|
| The Company’s operating activities | Taiwan | Short-term |
Response Measures
- Implementation of ISO 14064-1 greenhouse gas inventory mechanism.
- Replacement of high-energy-consuming equipment (including LED lighting equipment).
- Installation of green energy equipment (including solar panels and energy storage equipment).
- Continue to monitor regulatory changes to assess potential future financial impacts.
R2 TECHNOLOGICAL RISK - UNCERTAINTY IN ENERGY TRANSITION POWER SUPPLY
Description of Risk
As a result of climate change, there is a growing preference in the market for sustainable processes and maintenance services. If a company fails to effectively implement energy transition measures, it could face risks such as an unstable power supply in the electrical grid, resulting in potential power outages or shortages. This, in turn, could disrupt operations, particularly for equipment with extended startup and shutdown times.
Financial Impact
- In the event of a power outage or electricity shortage, operations may be disrupted.
- Increased costs from installing green energy equipment and replacing high-energy-consuming equipment.
| Affected Parties | Location | Timing of Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Upstream supply chain | Taiwan | Short-term |
Response Measures
- Adjusting the usage and charging times of high-energy-consuming equipment to off-peak hours (e.g. late at night) to avoid power outages caused by unstable supply and reduce electricity costs.
- Installed Phase II rooftop solar photovoltaic (PV) systems at the Guanyin Branch to achieve onsite self-generation and consumption.
- Equipped the plant with emergency power generation systems to respond to unexpected power outages.
- Adjusted production line schedules to shift operations during off-peak hours, thereby alleviating electricity demand during peak periods.
R3 REPUTATIONAL RISK - UNREALIZED CLIMATE GOALS
Description of Risk
Failure to adequately address climate issues and proactively respond to customers’ sustainability expectations may result in obstacles to business acquisition, potentially impacting revenue performance. Changes in investor attitudes may also reduce access to funding.
Financial Impact
- Failure to actively respond to customers, leading to potential customer loss and reduced revenue.
- Increased costs from installing green energy equipment and replacing high-energy-consuming equipment.
- The expansion and ongoing updates of verification items will lead to increased cost expenditures.
| Affected Parties | Location | Timing of Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Investment | Taiwan | Short-term |
Response Measures
- Implementation of ISO 14064-1 greenhouse gas inventory mechanism.
- Replacement of high-energy-consuming equipment (including LED lighting equipment).
- Installation of green energy equipment (including solar panels and energy storage equipment).
- Gradually implement quantitative financial assessments of climate risks.
- Respond promptly to customer questionnaire requests and actively enhance climate-related disclosures.
R4 PHYSICAL RISK - IMPACT OF EXTREME WEATHER
Description of Risk
The intensification of extreme weather events, such as polar vortex-induced snowstorms in the U.S. or typhoons in Taiwan, may lead to flight cancellations, diversions, or damage to operational facilities, directly or indirectly disrupting EGAT’s operations through its supply chain.
Financial Impact
- Disruption in the transportation of raw materials due to extreme weather conditions may lead to delayed deliveries, customer demands for compensation, or loss of orders, increasing operating costs.
- Damage to operational equipment and assets due to extreme weather impact.
| Affected Parties | Location | Timing of Impact |
|---|---|---|
| The Company’s operating activities | Americas / Europe / Taiwan / China | Short-term |
Response Measures
- Seeking and procuring alternative sources of supply to minimize the risk of manufacturing schedule disruption due to delayed aircraft material deliveries.
- Developing alternative maintenance methods, such as adjusting maintenance sequences to prioritize aircraft with all parts and materials ready, to mitigate the impact of delayed aircraft material deliveries on maintenance schedules.
- Establishing disaster prevention measures at manufacturing sites and implemented typhoon preparedness protocols in accordance with standard guidelines to minimize equipment damage, personnel injury, and financial losses caused by typhoons.
- Investing in disaster insurance to reduce potential financial losses resulting from typhoon impacts.
O1 RESOURCE USE EFFICIENCY - IMPROVEMENT OF ENERGY EFFICIENCY
Description of Opportunity
Reduce energy waste in operations, replace outdated/aging equipment in office buildings, or introduce smart energy management systems to reduce overall greenhouse gas emissions generated by the Company.
Financial Impact
- Increase energy efficiency to reduce the energy costs generated by the Company’s operations.
| Affected Parties | Location | Timing of Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Affected Parties Location Timing of Impact The Company’s operating activities | Taiwan | Short-term |
Response Measures
- Replace outdated high-bay lights in the hangars.
- Replace outdated chillers.
O2 RESOURCE USE EFFICIENCY - DEVELOPMENT OF CIRCULAR ECONOMY
Description of Opportunity
Through reliability assessment technology improvements on the maintenance side, accurately assess the safe operating time of aircraft equipment to avoid premature scrapping. On the manufacturing side, recycle metal scraps and other resources to improve resource utilization efficiency and reduce carbon emissions from waste disposal.
Financial Impact
- Enter the waste recycling market to increase revenue.
| Affected Parties | Location | Timing of Impact |
|---|---|---|
| The Company’s operating activities | Taiwan / Americas | Short-term |
Response Measures
- Recycling and selling scraps left over from processing for reuse.
O3 RENEWABLE ENERGY DEVELOPMENT - RENEWABLE ENERGY DEVELOPMENT
Description of Opportunity
Increase the proportion of renewable energy use. Increase the use of renewable energy through self-generation and self-use or procurement, or sell renewable energy to create additional business income for the Company.
Financial Impact
- Use solar energy for self-generation and self-use to reduce energy purchase costs.
- Enter the renewable energy market to increase revenue.
| Affected Parties | Location | Timing of Impact |
|---|---|---|
| The Company’s operating activities | Taiwan | Short-term |
Response Measures
- Construct new solar PV system and transition from “selling surplus electricity” to investing in self-generation and self-use solar energy development starting from 2024, to reduce energy costs and increase income.
CLIMATE SCENARIO ANALYSIS AND RESPONSE STRATEGIES
In 2024, EGAT conducted its first climate scenario analysis to enhance the quantitative assessment of the financial impacts of material climate-related risks and opportunities. Taking into account the appropriateness of a first-time assessment and the potential operational impact of each risk and opportunity, the analysis focused on one physical risk, one transition risk, and one opportunity, in order to evaluate the financial implications of climate change and to inform strategic planning for improving climate resilience.
TRANSITION RISK: CARBON MARKET MECHANISM AND REGULATORY CHANGES
Scenario Assumptions:
- Temperature Scenario: Stated Policies Scenario (STEPS)
- Time Horizon: Short-term (1–5 years), with analysis based on the year 2030
- Impact Scope: EGAT’s own operations, covering all sites and offices in Taiwan
Scenario Description and Parameters Used:
This scenario follows the Climate Change Response Act and evaluates potential costs under future carbon fee mechanisms, considering how various carbon-reduction pathways would affect EGAT’s greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions in 2030 and the resulting financial impact. The evaluation incorporated current policy trends, carbon pricing forecasts, and simulations of emission levels and carbon fee expenditures under different scenarios.
- According to the Executive Yuan’s draft “Fee-Charging Rates of Carbon Fees,” the carbon fee rate projected for 2030 is expected to range from NT$1,200 to NT$1,800 per tCO₂e.
- Reduction Pathway 1: No Mitigation Actions
If no additional GHG reduction measures are taken and emissions remain at the 2023 baseline level, regulatory tightening and changes in carbon market mechanisms may result in increased operational costs by 2030. - Reduction Pathway 2: Achieving Reduction Targets
By implementing carbon-reduction measures, EGAT aims to achieve its 2030 GHG intensity reduction target of 1.00 tCO₂e per NT$1 million in revenue. Under this scenario, with enhanced carbon market mechanisms and regulatory tightening, EGAT would be subject to lower carbon fee expenditures compared to a business-as-usual pathway.
Analysis Results:
- Reduction Pathway 1: Estimated financial impact equivalent to 0.134%–0.201% of 2030 revenue
- Reduction Pathway 2: Estimated financial impact equivalent to 0.120%–0.180% of 2030 revenue
Response Strategies:
To mitigate the impact of transition risks on operations, EGAT has actively promoted climate risk mitigation actions. In 2023, the Company officially adopted the ISO 14064 greenhouse gas inventory system and concurrently launched decarbonization initiatives, including the replacement of high energy-consuming equipment and installation of high-efficiency energy-saving systems, to directly reduce GHG emissions from operations. In 2024, EGAT continued to scale up its carbon-reduction efforts, with a total investment of NT$21.796 million in mechanism implementation, equipment replacement, and renewable energy installation, thereby demonstrating its strong commitment to sustainable development and low-carbon transformation.
PHYSICAL RISK: IMPACT OF EXTREME WEATHER
Scenario Assumptions:
- Temperature Scenario: SSP5-8.5 (global warming of 4.3°C)
- Time Horizon: Short-term (1–5 years), with analysis based on the year 2030
- Impact Scope: EGAT’s own operations, covering all sites and offices in Taiwan
Scenario Description and Parameters Used:
Under the SSP5-8.5 high-emissions scenario, the frequency of super typhoons is projected to increase, leading to heightened climate risks for EGAT’s operating sites. Extreme rainfall events could cause equipment and machinery damage, resulting in asset losses. In addition, heavy rainfall may carry excess sediment into reservoirs, raising turbidity and potentially disrupting water treatment operations, thus impacting the Company’s business continuity. During typhoons, EGAT must strengthen manpower allocation to respond to operational disruptions. As the frequency of super typhoons increases, the demand for manpower allocation during emergencies is expected to rise, further driving up operational costs.
- Flood Risk Assessment: According to the Climate Change Risk and Adaptation Platform, under the SSP5-8.5 scenario, facilities located in flood-prone areas could suffer asset value impairment during extreme rainfall events (defined as 650 mm within 24 hours) projected to occur by 2030.
- Extreme Rainfall Frequency: Each super typhoon is assumed to result in one extreme rainfall event. The projected frequency of such events in 2030 was estimated based on statistical data from the Climate Change Risk and Adaptation Platform and research published by the National Science and Technology Center for Disaster Reduction (NCDR).
- The primary impact of typhoons on operations was estimated using data from past typhoon events, including equipment repair costs and temporary labor costs for emergency response teams.
- It was assumed that each typhoon causes one full day of operational disruption.
Analysis Results:
- The estimated total financial impact from extreme weather events in 2030 is approximately 0.238% of projected annual revenue.
Response Strategies:
To reduce the operational impact of extreme climate events, EGAT has actively implemented adaptation strategies aimed at directly strengthening disaster response capacity and operational resilience. In terms of maintenance management, the Company developed alternative repair arrangements. On one hand, it implemented a shift system and enforced handover protocols to mitigate operational losses caused by extreme weather-related work stoppages. On the other hand, it coordinated with customers to reschedule aircraft and product delivery timelines, ensuring operational flexibility for the Company. The development of alternative repair methods primarily affects manpower allocation and does not involve additional cost expenditures. In addition, EGAT has installed disaster prevention infrastructure at its facilities to reduce the risks of flooding and water supply interruption, as well as to minimize equipment damage and the likelihood of operational disruption. In 2024, the total investment in climate adaptation measures amounted to approximately NT$709 thousand. The Company will continue to enhance its capacity to respond to climate-related risks in the years ahead.
OPPORTUNITIES: RENEWABLE ENERGY DEVELOPMENT
Scenario Assumptions:
- Temperature Scenario: Stated Policies Scenario (STEPS)
- Time Horizon: Short-term (1–5 years), with analysis based on the year 2030
- Impact Scope: EGAT’s own operations, covering all sites and offices in Taiwan
Scenario Description and Parameters Used:
To evaluate the impact of solar PV power generation on EGAT’s operating costs and benefits in 2030, the Company conducted an internal analysis to estimate the total renewable energy generation for that year. By referencing Taiwan Power Company’s industrial electricity pricing trends, the analysis assessed the potential financial opportunities and cost-saving benefits that solar energy may bring. In addition, EGAT conducted a supplementary assessment of operation and maintenance expenses and the amortized capital investment in solar PV equipment for the year, to evaluate whether the investment would be cost-effective.
- The Company aims to achieve 100% onsite renewable energy generation and consumption by 2030, thereby reducing electricity expenses and lowering overall operating costs.
- Estimated 2030 Industrial Electricity Rate by Taipower: Using the 2025 industrial electricity rate of NT$4.29/kWh, as announced by the Ministry of Economic Affairs, along with Taiwan’s projected energy mix and the IEA’s projected electricity cost trends, EGAT estimated the electricity rate under the 2030 national energy structure target.
Analysis Results:
- The total estimated benefit from renewable energy adoption in 2030 is projected to account for approximately 0.097% of annual revenue.
- Based on the Executive Yuan’s “Guidelines for the Useful Life of Fixed Assets,” the cost of installation of solar PV power generation equipment was amortized, and annual operation and maintenance costs were included. The estimated management cost associated with renewable energy investments is projected to account for approximately 0.047% of 2030 revenue.
Response Strategies:
EGAT continues to advance the installation of solar PV systems to increase the use of renewable energy and reduce operational greenhouse gas emissions, thereby contributing to the mitigation of climate change. In 2024, the Company invested NT$21,796 thousand to install an additional 499.29 kW of solar PV capacity and performed maintenance on existing facilities. Notably, the 499.29 kW system was the first to adopt a self-generation for self-use model, further enhancing renewable energy utilization efficiency. In 2025, EGAT plans to install an additional 1,204.91 kW of solar PV capacity, continuing its transition toward low-carbon operations.
INDICATORS AND TARGETS
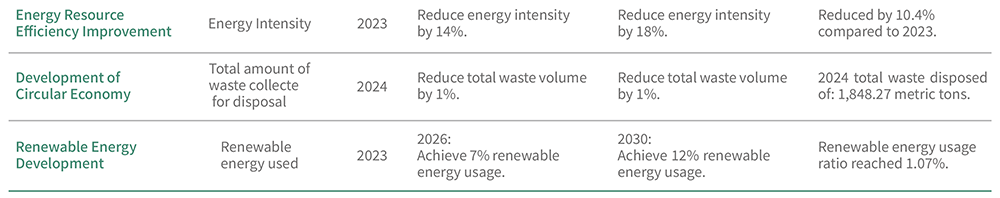
ENERGY AND GREENHOUSE GAS MANAGEMENT
GREENHOUSE GAS EMISSIONS STATISTICS
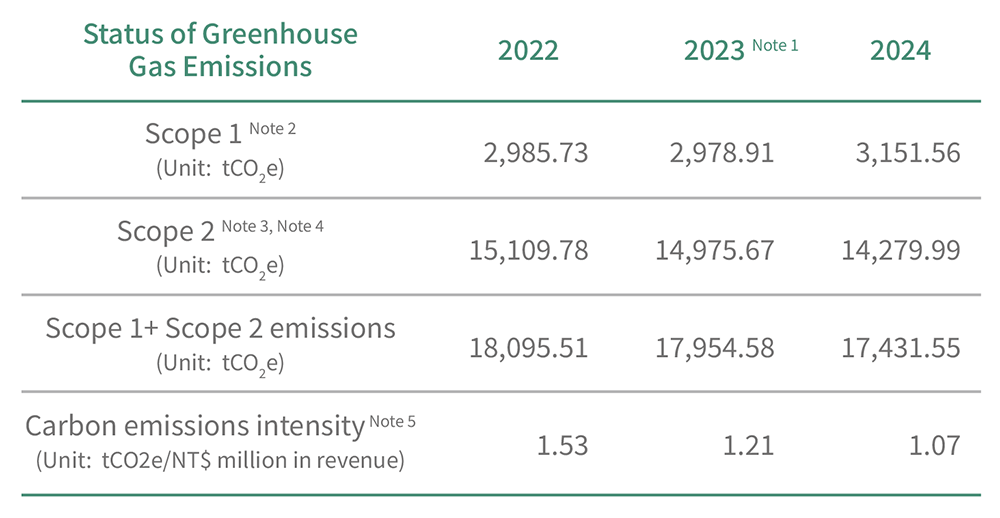
Note 2: GHG emissions were calculated using the operational control method for inventory, with the calculation method being activity data * emission factor * GWP value (emission factor values refer to the 2019 Environmental Protection Administration’s GHG emission factor management table version 6.0.4, and GWP values refer to the IPCC Sixth Assessment Report (2021)). GHG gases include carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs), perfluorocarbons (PFCs), sulfur hexafluoride (SF6), and nitrogen trifluoride (NF3).
Note 3: Since the 2024 electricity emission factor had not been announced at the time of conducting the 2024 GHG inventory, EGAT applied the 2023 emission factor of 0.494 kgCO₂e/kWh as the inventory standard. The 2023 inventory was also evaluated using the 2023 electricity emission factor of 0.494 kgCO₂e/kWh. In 2022, Guanyin Branch referenced the Energy Policy and Planning Office’s announcement of the 2021 electricity emission factor of 0.509 kgCO₂e/kWh, while Dayuan Maintenance Facility referenced the 2022 electricity emission factor announcement of 0.495 kgCO₂e/kWh. This was because, when conducting the 2022 greenhouse gas inventory, the 2022 electricity emission factor had not yet been published, so the 2021 factor was used as the inventory standard.
Note 4: In 2022, the Scope 2 GHG inventory of EGAT Guanyin Branch included electricity consumption from its investee company (Ever Superior Technologies Corporation). Starting in 2023, electricity consumption from the investee company (Ever Superior Technologies Corporation), and GHG emissions from the Taoyuan Airport leased office and TSA Maintenance Department have been included. Note 5: Emissions intensity = Scope 1 plus Scope 2 carbon emissions/NT$ million revenue.
In 2024, EGAT’s total energy consumption amounted to 141,468.36 gigajoules (GJ).
Based on EGAT’s energy consumption data over the past three years, total energy consumption in 2024 showed a downward trend and was the lowest among the three years. Despite ongoing business growth and an expanded inventory boundary since 2023, energy intensity decreased from 9.70 GJ per NT$1 million in 2023 to 8.69 GJ in 2024, representing a 10.40% year-on-year reduction—demonstrating a clear improvement in energy utilization efficiency.
THE COMPANY’S ENERGY CONSUMPTION DATA FOR THE MOST RECENT THREE YEARS
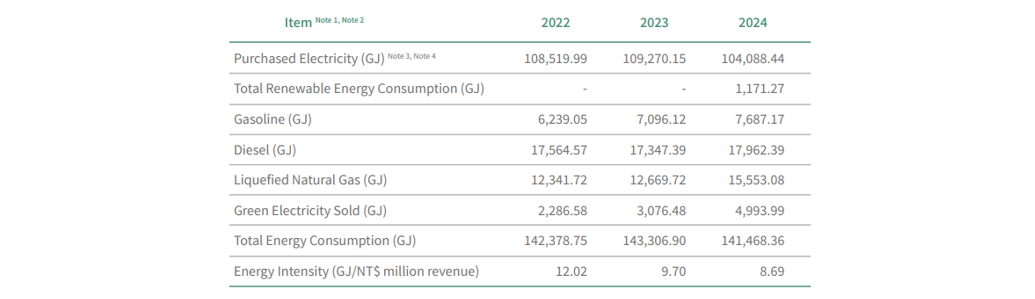
Note 2: EGAT previously calculated energy consumption using the calorific values provided in version 6.0.4 of the Environmental Protection Administration GHG Emission Factor Management Table. To align with the SASB Standards, the Company has adopted gross calorific values (GCV) starting in 2023 for energy consumption derived from fuels and biofuels, and retroactively adjusted past data to ensure consistency. The primary items affected were gasoline, diesel, and liquefied natural gas. Compared to previously reported data, energy consumption from gasoline in 2022 and 2023 increased by 43%, diesel by 28%, and liquefied natural gas by 19%. This adjustment reflects only a change in the calorific value coefficients and does not affect previously reported activity data.
Note 3: In 2022, the energy consumption of EGAT Guanyin Branch was the same as the Scope 2 inventory scope of GHG inventory, so the electricity usage of Ever Superior Technologies Corporation is included in the statistics. The 2023 scope excluded the electricity consumption of Ever Superior Technologies Corporation and included the GHG emissions from the Taoyuan Airport leased office and TSA Maintenance Department.
ANNUAL CARBON REDUCTION MEASURES AND RESULTS
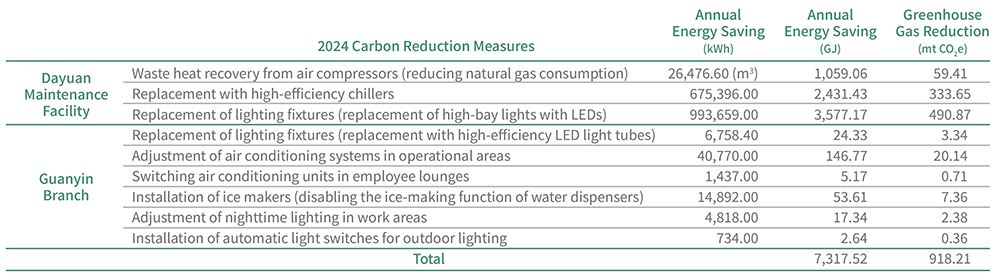
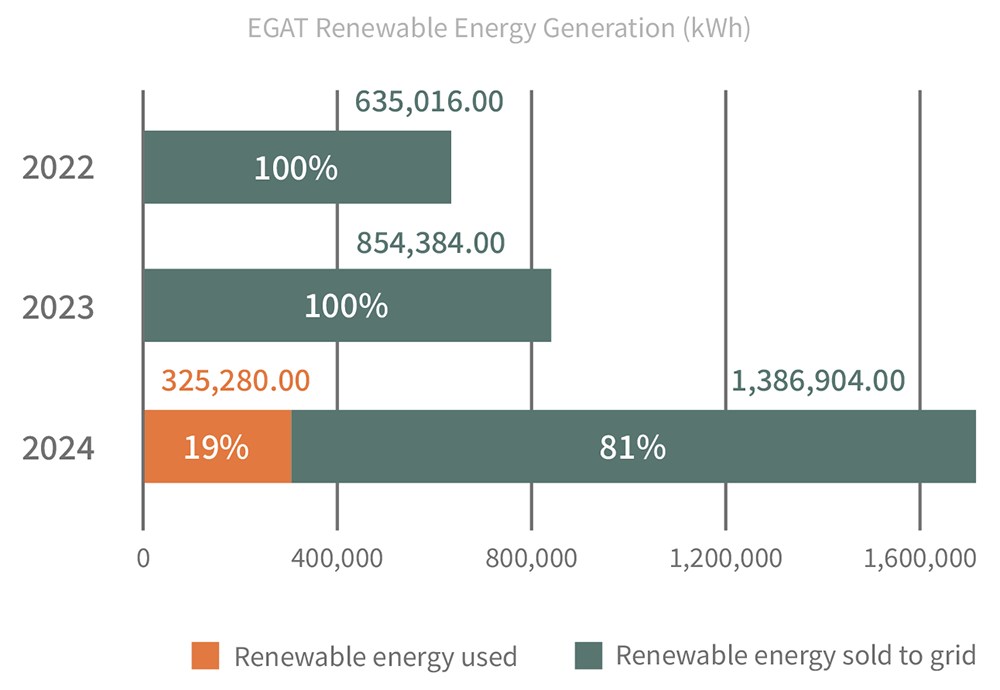
RENEWABLE ENERGY DEVELOPMENT
EGAT adjusted its solar development strategy in 2024, shifting to a self-generation for self-use model. A 499.29 kW solar PV system was installed on the rooftop of the third floor of the Guanyin Branch, allowing renewable energy to directly support the plant’s electricity demand. Total solar power generation reached 325,280.00 kWh in 2024, with the self-use ratio of renewable energy rising to 19.00%.